Introduction to Fungal Skin Infections
Fungal skin infections are common conditions caused by various types of fungi. These infections can affect different body parts, leading to discomfort and visible skin issues. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of fungal skin infections can help manage and prevent them effectively.
What is a Fungal Skin Infection?
A occurs when fungi invade the outer layers of the skin, leading to irritation, redness, and other symptoms. The fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, making certain body areas, such as the feet and groin, more susceptible.
Overview of Common Fungal Skin Diseases
Some of the most common fungal skin infections include athlete’s foot, jock itch, ringworm, and yeast infections. Each type of infection can affect specific body areas and presents with unique symptoms.
Causes of Fungal Skin Infections
Reason for Fungal Infection
Fungi naturally live on the skin in small amounts, but certain conditions can cause them to multiply and lead to infection. Poor hygiene, excessive sweating, weakened immune systems, and the use of antibiotics are common factors that contribute to fungal infections.
Types of Fungi that Cause Skin Infections
Different fungi are responsible for skin infections, including:
- Dermatophytes: These fungi cause conditions like ringworm and athlete’s foot.
- Yeast (Candida): Candida species can lead to yeast infections, commonly affecting moist areas of the skin like the groin or underarms.
Common Risk Factors
- Sweating excessively: Moist environments encourage fungal growth.
- Wearing tight clothing: This can trap moisture and lead to fungal infections.
- Weakened immune system: People with compromised immune systems are more prone to infections.
- Sharing personal items: Towels, clothing, and bedding can spread fungal infections.
Symptoms of Fungal Skin Infections
General Fungal Infection Symptoms
White fungus, caused by Candida, often results in:
- White, creamy patches on the skin or mucous membranes
- Pain and irritation, especially in the mouth, groin, or underarms
- In severe cases, systemic infections affecting internal organs
Fungal Infection on Face, Legs, and Other Areas
Fungal infections can affect various parts of the body, including the face and legs. These areas may present with symptoms like redness, irritation, and flaky skin. On the face, fungal infections can be mistaken for other skin conditions like eczema or acne.
Types of Fungal Skin Infections
Types of Fungal Infections (Ringworm, Athlete’s Foot, Jock Itch, etc.)
- Ringworm (Tinea corporis): Characterized by circular, red patches on the skin.
- Athlete’s Foot (Tinea pedis): Affects the feet, causing peeling, itching, and blistering.
- Jock Itch (Tinea cruris): Affects the groin area, causing red, itchy rashes.
- Yeast Infections: Often appear in moist areas, such as the underarms or groin, leading to redness and discomfort.
Skin Fungus and Its Impact
Fungal infections, though typically not serious, can cause significant discomfort. In some cases, untreated fungal infections can spread to other areas of the body or become chronic, leading to repeated flare-ups.
Mycoses: Different Forms of Fungal Infections
- Superficial mycoses: Infections that affect the skin, hair, or nails.
- Cutaneous mycoses: Fungal infections affecting deeper layers of the skin.
- Subcutaneous mycoses: These infections penetrate below the skin’s surface, often resulting from trauma.
Diagnosing Fungal Skin Infections
Signs to Watch For
Common signs of fungal skin infections include:
- Red, itchy, or scaly patches on the skin
- Unexplained rashes, particularly in moist areas
- Peeling skin between toes or on the soles of the feet
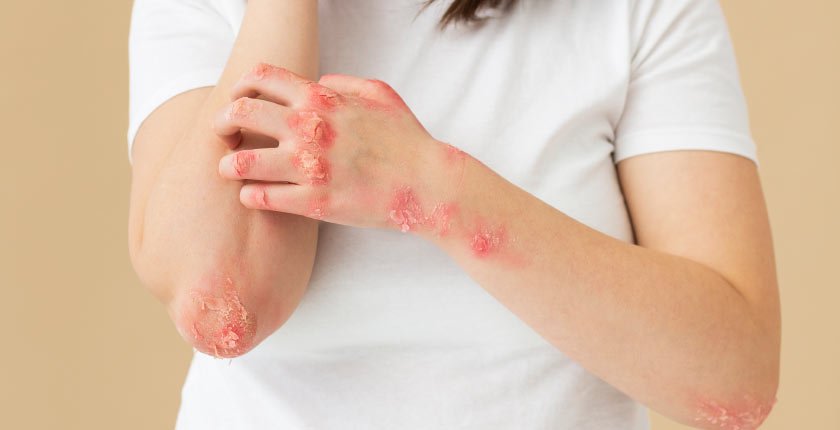
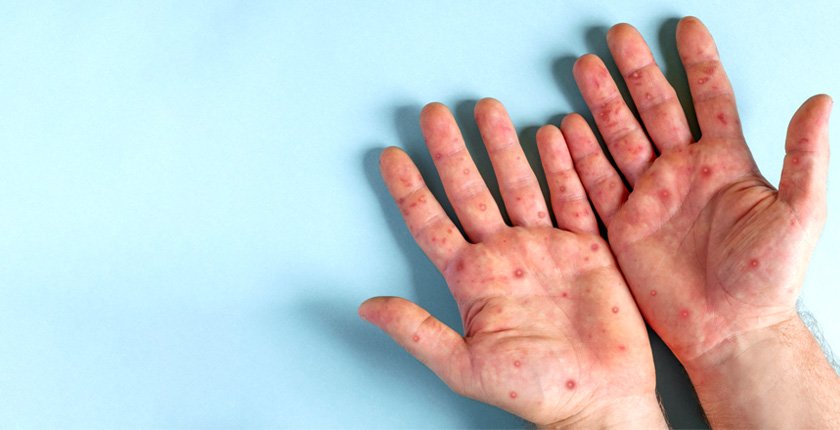
Skin Fungal Infection Pictures for Identification
Visual identification of fungal infections can be helpful for diagnosis. Ring-shaped patches, scaly feet, or red rashes in the groin area are some typical presentations. Consulting with a dermatologist and reviewing images can aid in self-diagnosis, but proper medical evaluation is crucial.
Treatments for Fungal Skin Infections
Medicine for Fungal Infections on Skin
Over-the-counter antifungal creams, ointments, or sprays can treat mild fungal infections. Some of the common active ingredients include clotrimazole, miconazole, and terbinafine.
Topical and Oral Treatments for Fungal Skin Infections
- Topical treatments: Creams and ointments are applied directly to the infected area.
- Oral medications: For severe or persistent infections, oral antifungal medications such as fluconazole or itraconazole may be prescribed.
Advanced Fungal Skin Infection Treatment Methods at Cutis Hospital
At Cutis Hospital, advanced treatments for fungal infections include:
- Prescription-strength antifungals: For more resistant infections.
- Laser treatments: Targeting deep fungal infections, especially nail fungus.
- Comprehensive care plans: Customized treatment approaches based on the severity and type of fungal infection.
Prevention of Fungal Skin Infections
Preventive Measures to Avoid Skin Fungal Infections
- Wear breathable clothing: Opt for loose, cotton clothes to reduce sweating.
- Use antifungal powders: Help absorb moisture and prevent infections in areas prone to sweating.
- Avoid walking barefoot in public places: Use sandals in communal showers and pool areas.
Hygiene Practices to Reduce Infection Risk
- Keep skin clean and dry: Fungi thrive in moist environments, so it’s essential to keep skin dry, especially in areas prone to sweating.
- Wash hands frequently: Proper hand hygiene can prevent the spread of fungal infections.
- Don’t share personal items: Avoid sharing towels, razors, and clothing with others to reduce the risk of infection
Conclusion
Fungal skin infections, though common are preventable and treatable. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments can help you manage and prevent these infections effectively. A expert dermatologists offer advanced care for fungal infections, ensuring quick recovery and long-term prevention.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.